Extraction of maxillary first molars in protrusive Class II division 1 malocclusion
Relato de Caso
INTRODUCTION: Class II, division 1 malocclusion is the most prevalent sub-classification, for which a number of treatments have been proposed over time. To treat Class II, division 1 in postpubertal patients, molar distalization, premolar extractions, fixed functional appliances, and surgical orthodontics can be used. Despite many efforts, anchorage loss may occur to varied degrees while applying distalization forces. The extraction of permanent maxillary first molars emerges as a feasible alternative to molar distalization.
Autores: Ekta Yadav, Mukesh Kumar Singh, Sugandha Sharma,

Você já deve ter percebido, quer seja por meio de artigos científicos ou por influência das mídias sociais, que há um número crescente de casos ortodônticos publicados/postados que foram tratados precocemente na idade infantil — nas dentições decídua e mista. E aí você poderia perguntar: mas qual a razão de haver esse provável aumento no número de pacientes tratados na infância? Estariam as más oclusões mais prevalentes nas crianças desse século, comparado ao século...
Leia mais
É com grande alegria que apresento a entrevista com a Profa. Isabela Almeida Shimizu, uma profissional de excelência na área da Ortodontia e da Harmonização Orofacial. Nossa amizade de mais de 20 anos me permite afirmar com segurança sobre sua competência e dedicação ímpar. A Profa. Isabela tem como primeira formação a Ortodontia, na qual é reconhecida por sua habilidade técnica e comprometimento com o bem-estar de seus pacientes. O Doutorado em Ciências da Saúde e as...
Leia mais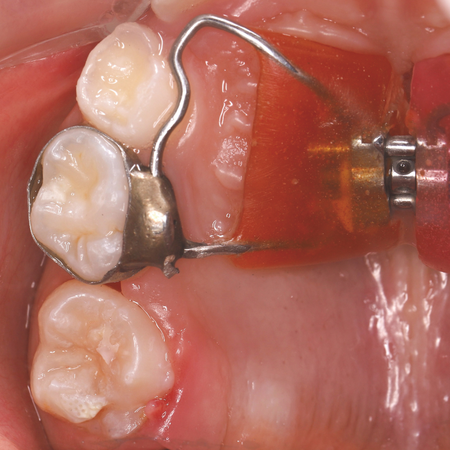
OBJETIVO: O objetivo deste artigo é apresentar um caso clínico de uma paciente, com 7 anos de idade, que fora submetido a expansão maxilar com o aparelho de Haas e, após 10 meses de acompanhamento, foi identificada erupção ectópica do primeiro molar permanente superior direito, por meio de uma radiografia panorâmica. RELATO DO CASO: O tratamento proposto foi usar o mesmo expansor para desimpactar o molar ectópico. O aparelho foi removido e soldou-se ao anel do segundo molar decíduo...
Leia mais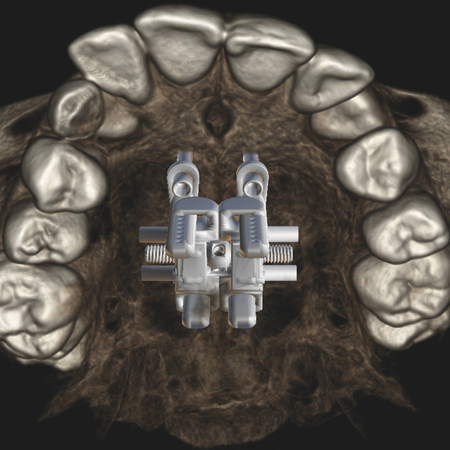
OBJETIVO: O presente estudo visou delinear um panorama abrangente das técnicas de expansão maxilar, desde os métodos pioneiros até as abordagens contemporâneas. Para isso, foram considerados aspectos tais como: diagnóstico por imagem, planejamento digital, variações anatômicas e os diversos designs de dispositivos de ancoragem esquelética (MARPE – Mini-implant assisted rapid palatal expansion). MÉTODOS: A seleção dos estudos foi realizada em ordem cronológica, permitindo uma...
Leia mais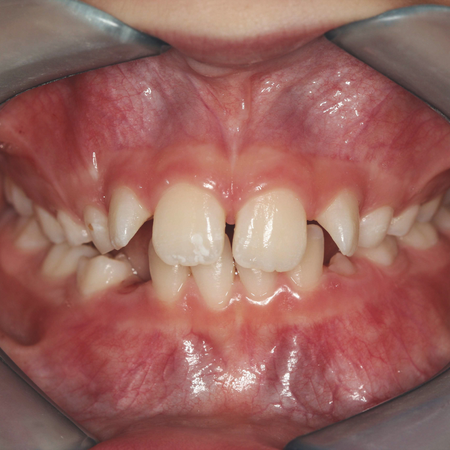
INTRODUÇÃO: Como a assimetria facial pode repercutir na estética da face e na função do sistema estomatognático do paciente, é de grande importância a abordagem precoce para prevenção da progressão das deformidades dentoesqueléticas. OBJETIVO: O objetivo deste relato de caso clínico foi descrever uma intervenção ortopédico- ortodôntica na fase de crescimento craniofacial, com o objetivo de proporcionar melhora na assimetria facial, incluindo correção do plano oclusal e má...
Leia mais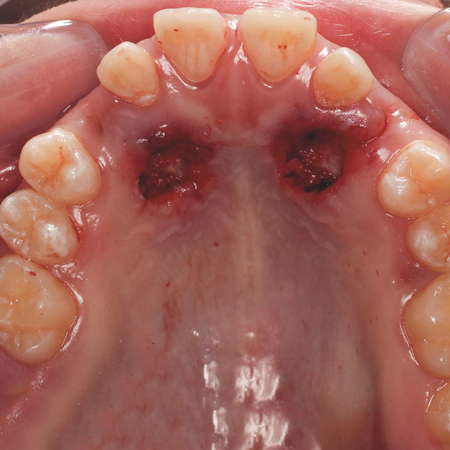
INTRODUÇÃO: Os caninos permanentes superiores estão entre os dentes mais frequentemente impactados, com uma prevalência variando entre 0,9% e 2,5%. A impacção geralmente ocorre no palato e pode ser causada por diversos fatores. Diferentes abordagens cirúrgicas têm sido propostas para o manejo dessa condição, incluindo técnicas de exposição fechada e aberta. A técnica de exposição aberta apresenta algumas vantagens, mas, em contrapartida, o cimento cirúrgico utilizado...
Leia mais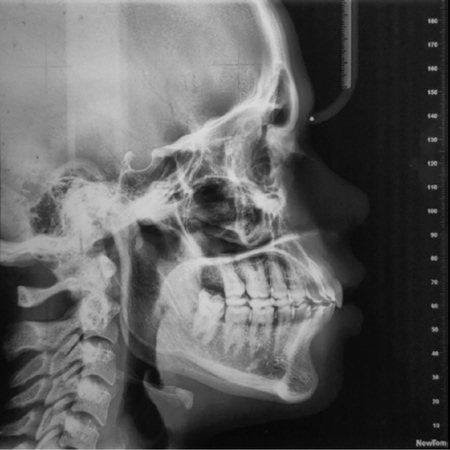
INTRODUÇÃO: A má oclusão de Classe II divisão 1 é a subclassificação mais prevalente, para a qual vários tratamentos foram propostos ao longo do tempo. Para tratar a Classe II, divisão 1 em pacientes pós-púberes, pode-se usar distalização de molares, extração de pré-molares, aparelhos funcionais fixos e tratamento ortodôntico-cirúrgico. Apesar dos esforços para evitá-la, a perda de ancoragem pode ocorrer em graus variados durante a aplicação de forças de distalização....
Leia mais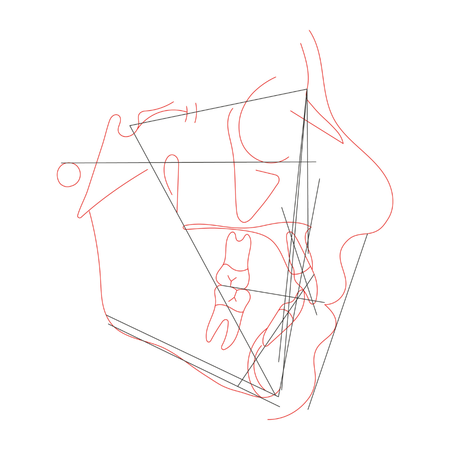
INTRODUÇÃO: A falta de espaço na arcada dentária e dentes mal posicionados são motivos que levam, com frequência, os pacientes a buscarem tratamento ortodôntico. Os incisivos inferiores frequentemente apresentam posicionamento incorreto nos casos de apinhamento dentário. A extração de um incisivo inferior pode ser uma forma de tratamento razoável, que contribui favoravelmente para a correção do apinhamento dentário inferior. OBJETIVO: O presente artigo aborda o tratamento de...
Leia mais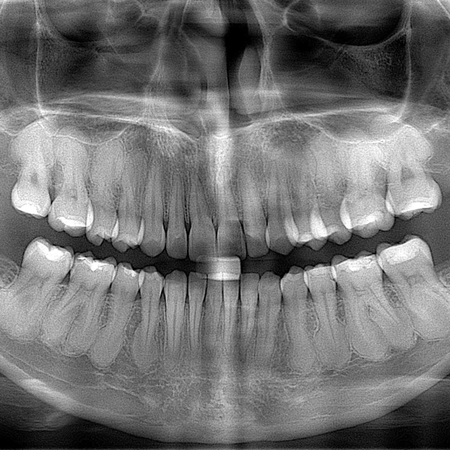
INTRODUÇÃO: O tipo mais frequente de hipercementose, quando moderada ou intensa, deixa o dente com a forma de clava. Nesses casos, não se deve movimentá-lo ortodonticamente, pois o formato da raiz dificulta ou impede a ação de forças no ligamento periodontal, que induziria os mecanismos biológicos da movimentação osteodentária. METODOLOGIA, RESULTADOS E DISCUSSÃO: Para diagnosticar se a hipercementose em forma de clava é moderada ou intensa, o critério proposto é traçar uma...
Leia mais
Es posible que haya notado, ya sea a través de artículos científicos o por la influencia de las redes sociales, que hay un número cada vez mayor de casos de Ortodoncia publicados que se trataron en la primera infancia, en las denticiones temporales y mixtas.
Leia mais
Es un gran placer presentar esta entrevista con la Profesora Isabela Almeida Shimizu, una profesional de excelencia en el campo de la Ortodoncia y la Armonización Orofacial. Nuestra amistad de más de 20 años me permite afirmar con seguridad su inigualable competencia y dedicación. La Profesora Isabela se formó principalmente en Ortodoncia, donde es reconocida por su habilidad técnica y compromiso con el bienestar de sus pacientes. Su Doctorado en Ciencias de la Salud y sus...
Leia mais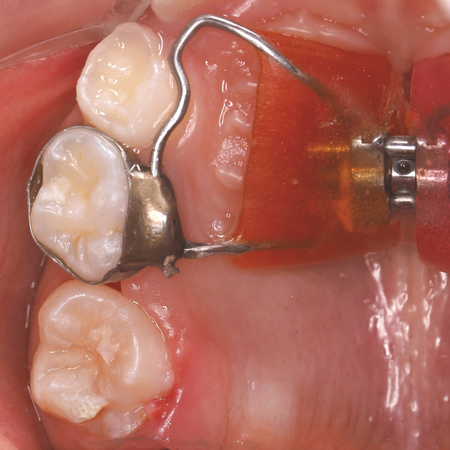
OBJETIVO: El objetivo de este artículo es presentar un caso clínico de una paciente de 7 años que fue sometida a expansión maxilar mediante un disyuntor de Haas y, tras 10 meses de seguimiento, se identificó una erupción ectópica del primer molar permanente superior derecho mediante radiografía panorámica. RELATO DEL CASO: Se propuso utilizar el mismo disyuntor como aparato para desimpactar el molar ectópico. El aparato fue retirado y se soldó una extensión de alambre rígido a...
Leia mais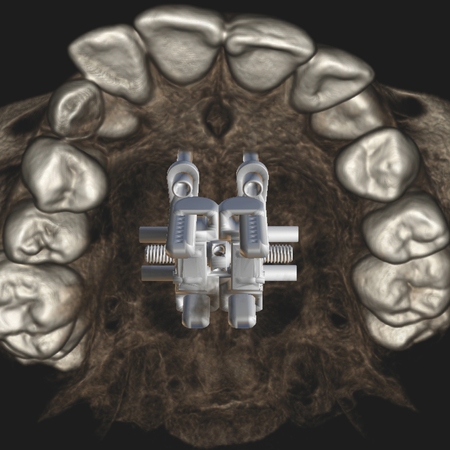
OBJETIVO: Este estudio tuvo como objetivo presentar una visión general de las técnicas de expansión maxilar, desde los métodos pioneros hasta los enfoques contemporáneos. Para ello, se consideraron aspectos como el diagnóstico por imagen, la planificación digital, las variaciones anatómicas y los diversos diseños de dispositivos de anclaje esquelético (MARPE – Mini-implant assisted rapid palatal expansion). MÉTODOS: Los estudios se seleccionaron en orden cronológico, lo que...
Leia mais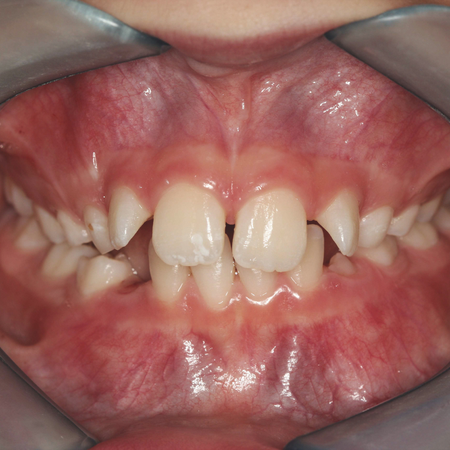
INTRODUCCIÓN: Debido a que la asimetría facial puede afectar la estética facial y la función del sistema estomatognático, el tratamiento temprano es crucial para prevenir la progresión de las deformidades dentoesqueléticas. OBJETIVO: Este reporte de caso describe una intervención ortopédica-ortodóncica durante la fase de crecimiento craneofacial para mejorar la asimetría facial, incluyendo la corrección del plano oclusal y la maloclusión de Clase II. MÉTODOS: El tratamiento...
Leia mais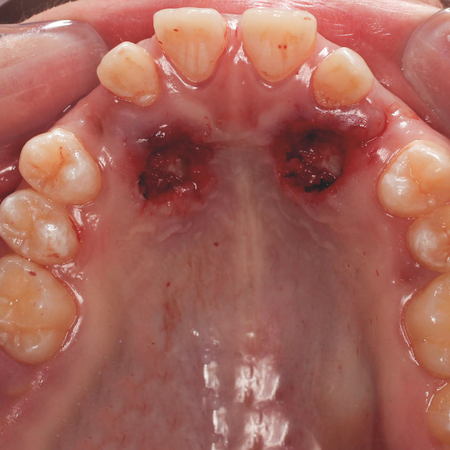
INTRODUCCIÓN: Los caninos permanentes superiores se encuentran entre los dientes impactados con mayor frecuencia, con una prevalencia que oscila entre el 0,9% y el 2,5%. La impactación suele ocurrir en el paladar y puede deberse a diversos factores. Se han propuesto diferentes abordajes quirúrgicos para el tratamiento de esta afección, incluyendo técnicas de exposición cerrada y abierta. La técnica de exposición abierta presenta algunas ventajas, pero, por otro lado, el cemento...
Leia mais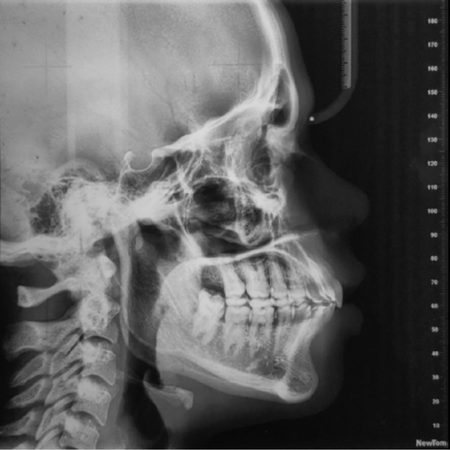
INTRODUCCIÓN: La maloclusión de Clase II, subdivisión 1, es la subclasificación más prevalente, para la cual se han propuesto diversos tratamientos. Para tratar la Clase II, subdivisión 1, en pacientes pospuberales, se pueden usar la distalización molar, la extracción de premolares, la aparatología funcional fija y el tratamiento orto-quirúrgico. A pesar de los esfuerzos para prevenirla, la pérdida de anclaje puede ocurrir en grados variados durante la aplicación de fuerzas de...
Leia mais
INTRODUCCIÓN: La falta de espacio en la arcada dental y la malposición dentaria son motivos comunes por los cuales los pacientes buscan tratamiento de Ortodoncia. Los incisivos inferiores suelen estar mal posicionados en casos de apiñamiento dental. La extracción de un incisivo inferior puede ser una opción de tratamiento razonable que contribuye favorablemente a la corrección del apiñamiento dental inferior. OBJETIVO: Este artículo aborda el tratamiento de una maloclusión de Clase...
Leia mais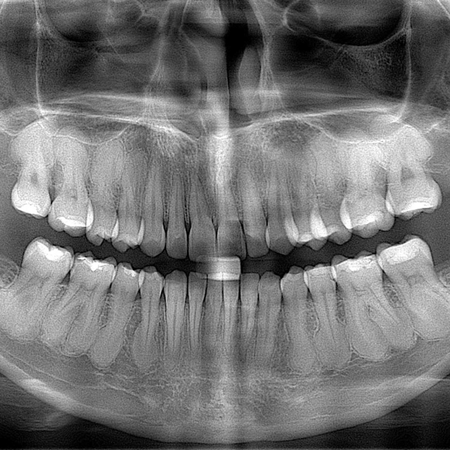
INTRODUCCIÓN: El tipo más común de hipercementosis, cuando es moderada o severa, deja el diente en forma de maza. En estos casos, no se debe realizar movimiento ortodóncico, ya que la forma de la raíz dificulta o impide la acción de fuerzas sobre el ligamento periodontal, lo que induciría los mecanismos biológicos del movimiento dental ortodóncico. METODOLOGÍA, RESULTADOS Y DISCUSIÓN: Para diagnosticar si la hipercementosis en forma de maza es moderada o severa, el criterio...
Leia mais
You may have noticed, whether through scientific articles or through the influence of social media, that there is a growing number of published/posted orthodontic cases that were treated early in childhood—in the deciduous and mixed dentitions. And then you might ask: but what is the reason for this likely increase in the number of patients treated in childhood? Are malocclusions more prevalent in children this century, compared to the last century?
Leia mais
It is with great joy that I present the interview with Professor Isabela Almeida Shimizu, a professional of excellence in the field of Orthodontics and Orofacial Harmonization. Our friendship of over 20 years allows me to confidently affirm her unparalleled competence and dedication. Professor Isabela’s first training is in Orthodontics, in which she is recognized for her technical skill and commitment to the well-being of her patients. Her PhD in Health Sciences and specializations in TMD...
Leia mais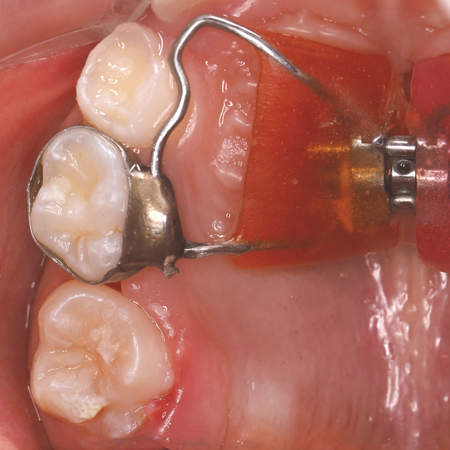
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this article is to present a clinical case of a 7-year-old patient who underwent maxillary expansion with the Haas expander and, after 10 months of follow-up, ectopic eruption of the upper right permanent first molar was identified using a panoramic radiograph. CASE REPORT: The proposed treatment was to use the same expander to disimpact the ectopic molar. The appliance was removed and a rigid wire extension was soldered to the ring of the deciduous second molar, with a...
Leia mais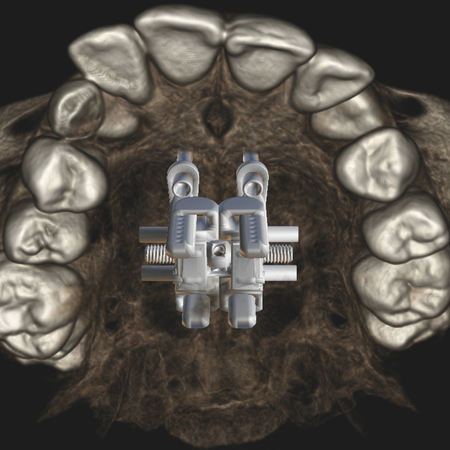
OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of maxillary expansion techniques, from the pioneering methods to contemporary approaches. This included aspects such as diagnostic imaging, digital planning, anatomical variations and the various designs of skeletal anchorage devices (MARPE - Mini-implant assisted rapid palatal expansion). METHODS: The studies were selected in chronological order, allowing a progressive and broad understanding of the advancement of the...
Leia mais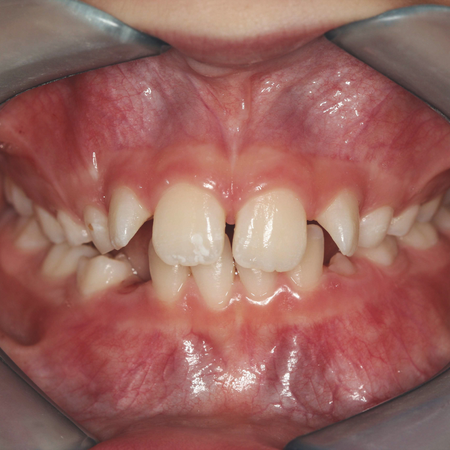
INTRODUCTION: As facial asymmetry can reverberate in the aesthetics of the face and in the stomatognathic system function of the patient, it is of great importance to have an early approach for preventing the progression of dentoskeletal deformities. OBJECTIVE: The objective of this clinical case report was to describe an orthopedic-orthodontic intervention in the phase of craniofacial growth, in order to provide improvement in the facial asymmetry, including correction of occlusal plane and...
Leia mais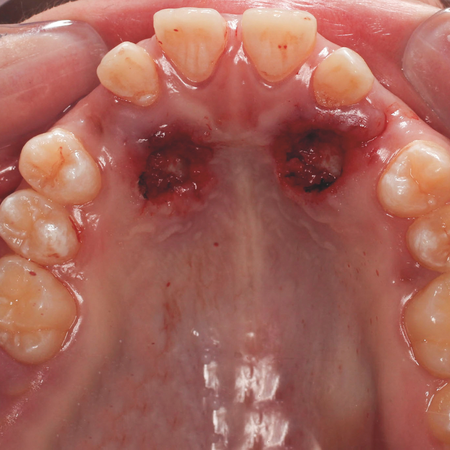
INTRODUCTION: Maxillary permanent canines are among the most frequently impacted teeth, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9% to 2.5%. The impaction usually occurs on the palate and is caused by various factors. Different surgical approaches have been proposed for the management of this dental impaction, including closed and open exposure techniques. The open exposure technique has some advantages, but on the other hand the surgical cement used has limitations, such as low adhesion to enamel...
Leia mais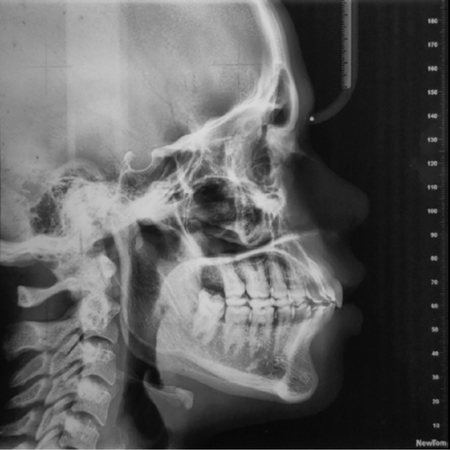
INTRODUCTION: Class II, division 1 malocclusion is the most prevalent sub-classification, for which a number of treatments have been proposed over time. To treat Class II, division 1 in postpubertal patients, molar distalization, premolar extractions, fixed functional appliances, and surgical orthodontics can be used. Despite many efforts, anchorage loss may occur to varied degrees while applying distalization forces. The extraction of permanent maxillary first molars emerges as a feasible...
Leia mais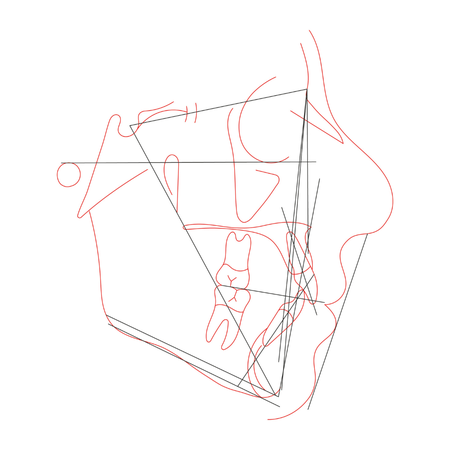
INTRODUCTION: Lack of space and malpositioned teeth are common reasons why patients seek orthodontic treatment. Lower incisors frequently present incorrect positioning in cases of dental crowding. The extraction of a lower incisor can be a reasonable treatment option that favorably contributes to correcting lower dental crowding. OBJECTIVE: This article reports the treatment of an Angle Class I malocclusion with crowding in the lower arch, managed through the extraction of a lower incisor...
Leia mais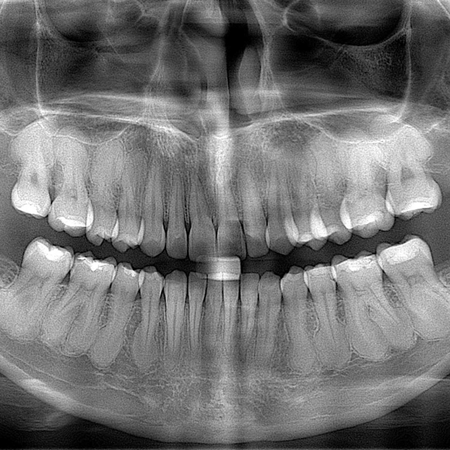
INTRODUCTION: The most common type of hypercementosis, when moderate or severe, leaves the tooth in the shape of a club. In these cases, orthodontic movement should not take place, as the shape of the root hinders or prevents the action of forces on the periodontal ligament that would induce the biological mechanisms of osteodental movement. METHODOLOGY, RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: To diagnose whether club-shaped hypercementosis is moderate or severe, the proposed criterion is to draw a tangent...
Leia maisCopyright © 1996 - 2024 DentalGO | Todos Direitos Reservados. DentalGO é uma marca Dental Press
Login